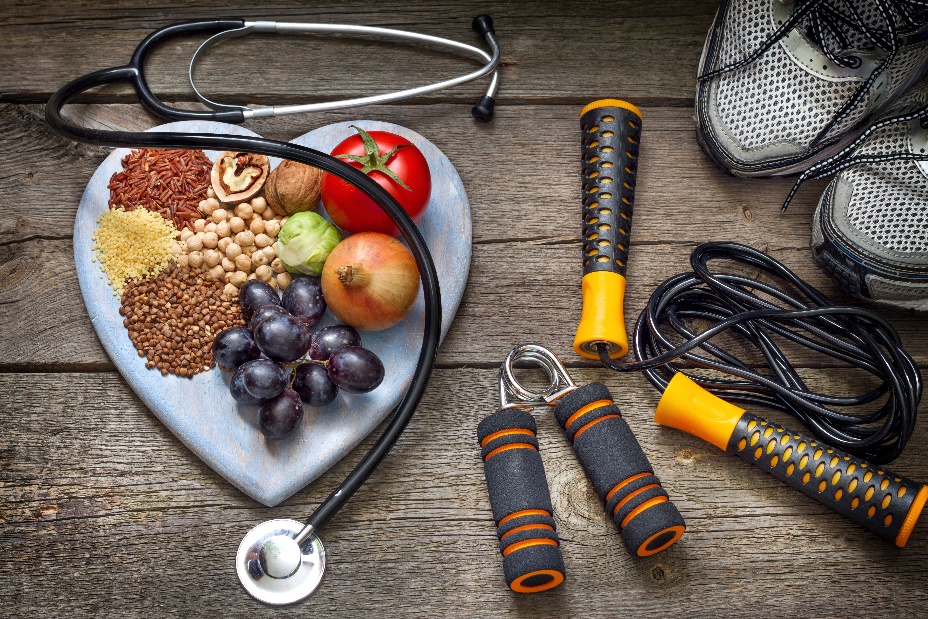
In today’s fast-paced world, where convenience often trumps health, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is more important than ever. But what does a healthy lifestyle truly mean? Simply put, it’s a balanced way of living that includes nutritious eating, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and mental well-being. Choosing to live healthily isn’t just about avoiding illness; it’s about enhancing your quality of life in countless ways. This article explores the numerous benefits of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and why it’s a choice worth making.
Key Takeaways
- A healthy lifestyle improves cardiovascular health, supports weight management, and boosts the immune system.
- Mental health benefits include reduced stress, better mood, and improved cognitive function.
- Healthy habits reduce the risk of chronic diseases and contribute to a longer, higher-quality life.
- Consistent physical activity and balanced nutrition are cornerstones of a healthy lifestyle.
- Small lifestyle adjustments can lead to significant health improvements over time.
- Mental well-being is as important as physical health in maintaining overall wellness.
- Overcoming barriers like time and motivation is key to sustaining healthy habits.
Physical Health Benefits
1. Improved Cardiovascular Health
One of the most significant benefits of a healthy lifestyle is better heart health. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins combined with regular exercise can reduce the risk of heart diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, and helps maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
2. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle helps regulate body weight by balancing calorie intake with physical activity. Being overweight or obese increases the risk of many chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and joint problems. A healthy lifestyle aids in achieving and sustaining a healthy weight, reducing these risks substantially.
3. Stronger Immune System
A nutritious diet and regular exercise boost your immune system, helping your body fend off illnesses more effectively. Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants found in healthy foods enhance immune responses, while physical activity promotes better circulation, allowing immune cells to move freely throughout the body.
4. Increased Energy and Vitality
Healthy habits can dramatically increase your energy levels. Nutrient-rich foods provide the necessary fuel for your body, and physical activity improves stamina and reduces feelings of fatigue. This vitality allows you to be more productive and enjoy your daily activities.
Mental Health Benefits
5. Reduced Stress and Anxiety
Exercise is a natural stress reliever as it releases endorphins, the body’s feel-good chemicals. Additionally, a healthy lifestyle that includes proper sleep and mindfulness practices can reduce anxiety levels and improve your ability to handle stress.
6. Better Mood and Cognitive Function
Eating balanced meals that support brain health — such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins — combined with physical activity can improve mood and cognitive functions. This means better memory, sharper focus, and reduced risks of cognitive decline and depression.
7. Improved Sleep Quality
Good sleep hygiene, a key part of a healthy lifestyle, helps regulate your body’s natural rhythms and improve overall sleep quality. Regular exercise and a balanced diet also contribute to better sleep patterns, allowing your body to repair and rejuvenate.
Long-Term Health Benefits
8. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
A healthy lifestyle significantly lowers the chances of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and osteoporosis. Prevention is better than cure, and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in disease prevention.
9. Longevity
People who maintain healthy habits tend to live longer. Studies consistently show that balanced diets, regular physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking contribute to increased life expectancy.
10. Enhanced Quality of Life
Beyond adding years to your life, a healthy lifestyle adds life to your years. It enables you to maintain independence as you age, reduces the likelihood of disability, and allows you to participate in social, recreational, and occupational activities with ease.
healthy lifestyle
1. How to Build a Balanced Diet for Optimal Health
Explore the essential components of a balanced diet — macronutrients, micronutrients, portion control, and meal timing. Include practical tips on meal planning, grocery shopping, and reading nutrition labels.
2. Top 10 Easy Exercises to Incorporate into Your Daily Routine
Discuss beginner-friendly exercises that can be done at home or outdoors, including walking, stretching, bodyweight workouts, and yoga. Explain the benefits of each and how to stay consistent.
3. The Role of Sleep in Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Dive into why quality sleep is crucial for physical and mental health. Cover sleep hygiene tips, how poor sleep affects the body, and ways to improve sleep patterns naturally.
4. Mental Health and Mindfulness: Tools for Everyday Well-being
Explain mindfulness practices like meditation, deep breathing, and journaling. Highlight how these techniques reduce stress, improve focus, and promote emotional resilience.
5. How to Manage Stress Through Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Detail how diet, exercise, sleep, and relaxation techniques can help manage stress. Include practical strategies such as time management, social support, and setting boundaries.
5 detailed health topics
1. Digital Wellness: How to Protect Your Health in a Hyperconnected World
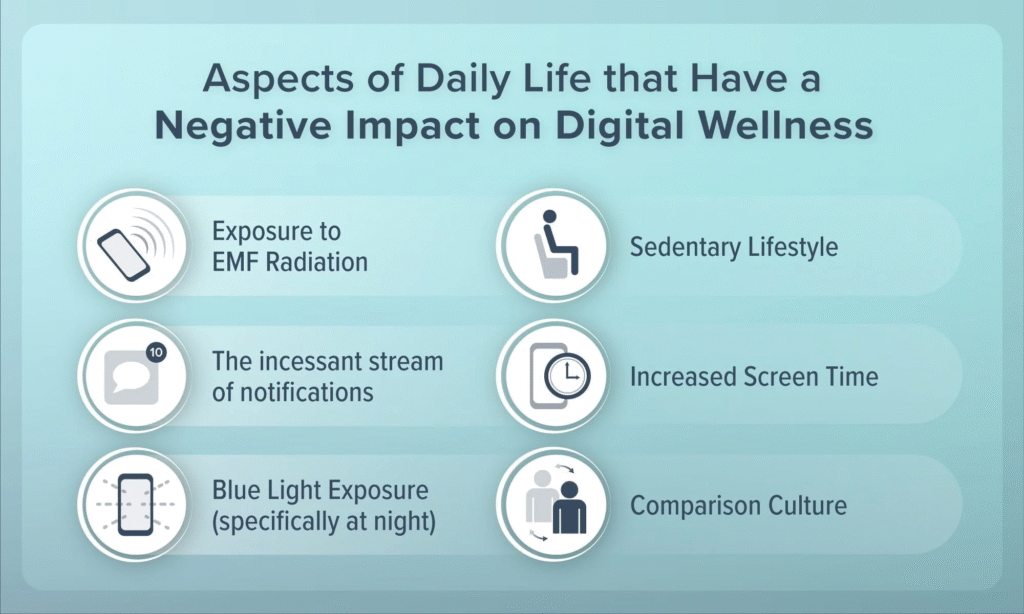
In today’s digital age, where smartphones, laptops, and wearable tech dominate our lives, digital wellness has emerged as a critical aspect of overall health. It refers to the intentional use of technology in a way that promotes physical, mental, and social well-being. While technology offers incredible benefits—such as access to healthcare information, fitness tracking, and remote work—it also poses serious risks when misused or overused.
Excessive screen time has been linked to sleep disorders, eye strain, neck and back pain, and decreased physical activity. Psychologically, it can lead to anxiety, depression, and reduced attention spans, especially among children and adolescents who are still developing emotionally. Social media platforms, in particular, contribute to comparison anxiety, cyberbullying, and digital addiction.
Digital wellness encourages practices like scheduled tech breaks, using blue light filters, practicing “digital minimalism,” and establishing screen-free zones or times (e.g., during meals or before bedtime). It also involves being mindful of online consumption, setting boundaries, and cultivating healthy digital habits.
As technology continues to evolve, teaching digital literacy and promoting digital wellness in schools, workplaces, and homes is essential. The goal isn’t to eliminate technology, but to create a sustainable balance that supports mental clarity, productivity, emotional regulation, and meaningful real-world connections.
2. The Importance of Mental Fitness: Training Your Mind Like a Muscle
Just as physical fitness is vital for the body, mental fitness is crucial for the brain. It refers to the ability to think clearly, manage emotions, stay resilient under pressure, and maintain psychological well-being. Mental fitness is not about never feeling stress or sadness—it’s about developing coping mechanisms and cognitive flexibility to handle life’s challenges effectively.
Mental fitness can be improved through daily practices such as mindfulness meditation, journaling, cognitive exercises, and learning new skills. Engaging in mental challenges like puzzles, reading, or creative activities can help sharpen memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills. Emotional regulation practices—like deep breathing, gratitude exercises, and positive self-talk—build resilience and prevent emotional burnout.
In today’s fast-paced world, where stress, multitasking, and information overload are common, mental fitness has become as important as cardio or strength training. Mental fatigue can lead to poor decision-making, irritability, low productivity, and even physical illness. In contrast, those with strong mental fitness tend to have better focus, higher emotional intelligence, and greater life satisfaction.
Organizations and educational systems are now recognizing the value of promoting mental fitness through wellness programs, stress reduction workshops, and mental health days. It’s time we treat mental fitness not as a luxury, but as a daily necessity—training our minds to be as resilient, flexible, and strong as our bodies.
3. Food as Medicine: How Nutrition Heals the Body
The concept of “food as medicine” is gaining ground as research continues to prove the powerful impact nutrition has on healing and preventing disease. Instead of viewing food simply as fuel or calories, this perspective treats food as a therapeutic tool that can support the body’s natural healing processes, reduce inflammation, boost immunity, and balance hormones.
Nutrient-rich whole foods—such as leafy greens, berries, nuts, legumes, fatty fish, and spices like turmeric and ginger—contain anti-inflammatory compounds, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help combat oxidative stress and chronic illness. Diets like the Mediterranean, DASH, or plant-based diets have been linked to lower rates of heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and certain cancers.
Conversely, diets high in processed foods, refined sugar, trans fats, and sodium contribute to systemic inflammation and a host of preventable diseases. These foods often lack essential nutrients and overload the body with harmful substances that stress organs, weaken the immune system, and disrupt metabolic processes.
Healthcare providers are increasingly integrating nutrition counseling into treatment plans and recommending diet as part of disease management. Some forward-thinking hospitals and clinics even have “food pharmacies” or partnerships with local farms to offer patients fresh produce.
“Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food,” said Hippocrates centuries ago—and it rings truer than ever. Embracing a food-as-medicine mindset empowers individuals to take control of their health, prevent illness before it starts, and build a stronger, more vibrant body from the inside out.
4. Social Health: The Overlooked Pillar of Well-being
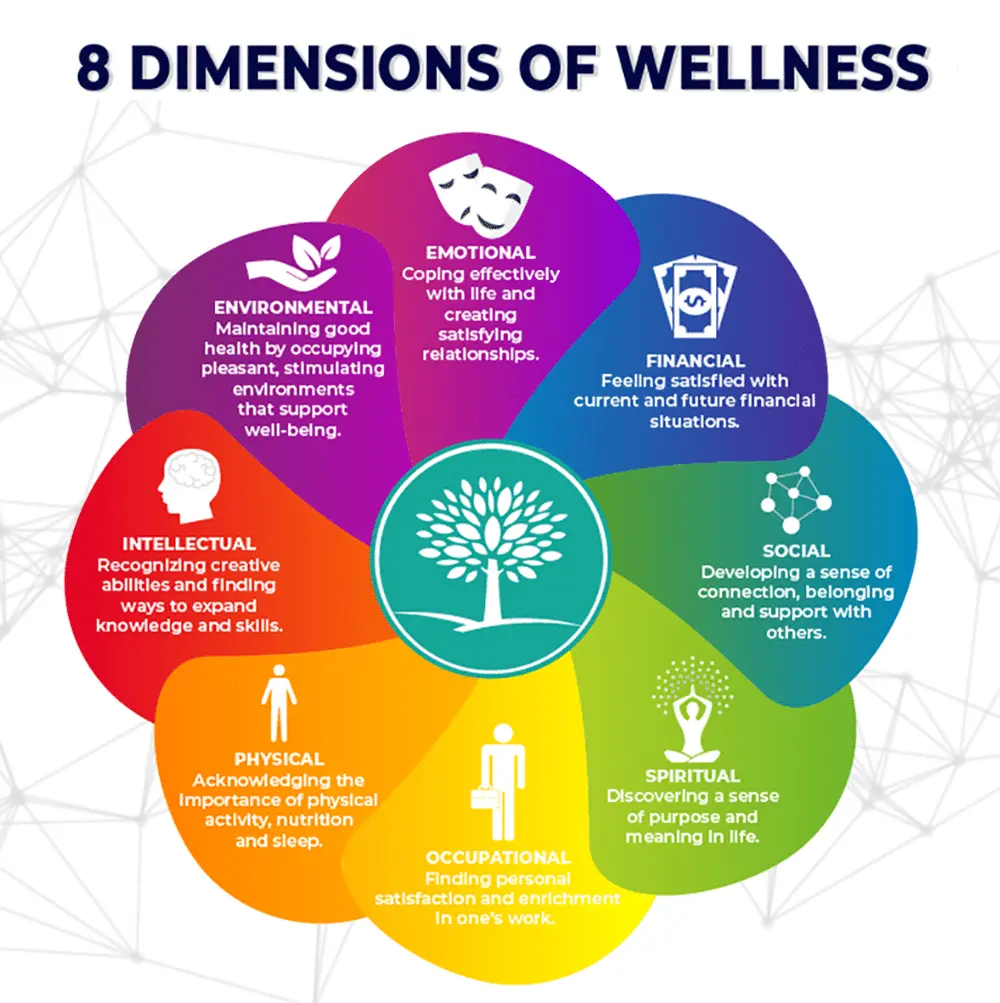
While physical and mental health often take center stage, social health—our ability to form and maintain meaningful relationships—is equally vital to overall well-being. Social connections influence everything from emotional stability to physical resilience. People who are socially connected tend to live longer, handle stress better, and experience lower rates of anxiety and depression.
Loneliness, on the other hand, has been dubbed the new smoking. Studies show that chronic loneliness is associated with increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, cognitive decline, and weakened immune function. In fact, the negative health effects of loneliness are comparable to smoking 15 cigarettes a day.
Social health is about quality, not quantity. It involves having supportive, respectful, and enriching relationships—with friends, family, coworkers, and the community. It also means feeling a sense of belonging, being able to communicate effectively, and navigating conflicts with empathy.
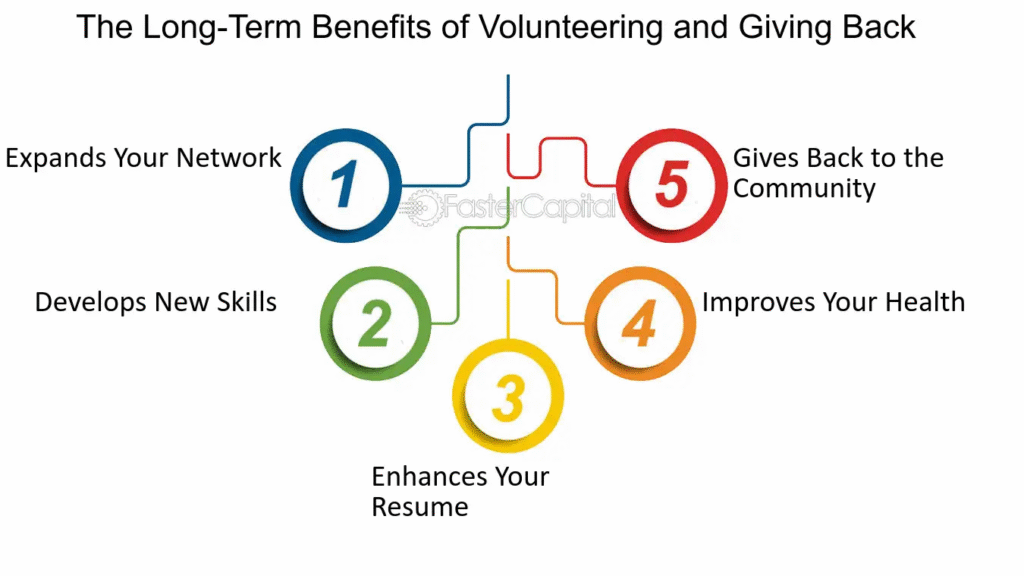
Improving social health can include joining clubs, volunteering, reaching out to old friends, or participating in local events. In a digital age, it also means balancing online interactions with real-world connection.
Governments and public health agencies are now recognizing loneliness as a health crisis and are implementing community programs to promote social engagement—especially among the elderly, disabled, and marginalized populations. Social health isn’t just a feel-good concept; it’s a biological necessity for a longer, healthier, and more fulfilling life.
5. The Healing Power of Nature: Why Time Outdoors Is Essential for Health
Nature isn’t just beautiful—it’s medicinal. The concept of “ecotherapy” or “green therapy” refers to spending time in natural environments to support physical and mental health. Studies have shown that regular exposure to nature reduces cortisol (stress hormone) levels, lowers blood pressure, improves mood, and even enhances immune function.
Time spent in green spaces has also been linked to decreased symptoms of depression, anxiety, and ADHD. Forest bathing—a Japanese practice called Shinrin-yoku—involves mindfully walking through forests, using all senses to absorb the environment. It’s proven to slow heart rate, promote calmness, and increase natural killer cell activity, which boosts immunity.
In urban environments, where people are often surrounded by concrete and screens, green spaces offer a much-needed retreat. Parks, gardens, walking trails, and even indoor plants can create moments of relaxation and mental clarity. Nature not only helps us slow down, but it also stimulates creativity, improves sleep, and promotes physical activity.
Children raised with regular access to nature show better emotional development, creativity, and academic performance. For adults, nature walks are associated with improved focus and decreased rumination—a marker of depression.
As cities become more densely populated, urban planning must prioritize green spaces for mental and public health. Whether it’s a daily walk in the park, weekend hikes, or even gardening, reconnecting with Nature is one of the most accessible, affordable, and effective ways to boost overall wellness
Also read : How to finance your MBA without going into debt
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is a powerful investment in your future well-being. It not only helps prevent many chronic diseases but also enhances your physical, mental, and emotional health. Small, consistent changes—like eating well, staying active, managing stress, and getting enough sleep—can transform your quality of life. Remember, the journey to health is personal, and every positive step counts.
FAQs
1. What is considered a healthy lifestyle?
A healthy lifestyle includes balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, stress management, and avoidance of harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
2. How much exercise should I get to maintain good health?
The World Health Organization recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week for adults.
3. Can a healthy lifestyle help manage chronic diseases?
Yes, many chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease can be managed and even prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
4. Is mental health part of a healthy lifestyle?
Absolutely. Mental well-being is integral to a healthy lifestyle. Practices such as mindfulness, adequate sleep, and physical activity support mental health.
5. How does diet affect a healthy lifestyle?
Diet is foundational. Consuming nutrient-dense foods provides energy, supports immune function, and reduces the risk of disease.
6. Can small lifestyle changes make a big difference?
Yes. Even small changes like drinking more water, taking daily walks, or improving sleep routines can significantly improve overall health over time.
7. What are the biggest barriers to maintaining a healthy lifestyle?
Common barriers include lack of time, motivation, access to healthy foods, and knowledge about health. Overcoming these requires planning, support, and education.
